FRM
국제 FRM Part 1 오답·개념 정리
khc9914
2024. 1. 4. 16:12
Chapter 1
Foundations of risk management
▶GARP Code of conduct
|
Disclosure of conflicts of interest
|
|
Follow local culture
|
|
Follow higher standard
|
|
Independence
|
|
Cannot outsource responsibilities
|
|
Clearly disclose limits of knowledge
|
|
Not overstating accuracy/certainty of result
|
▶Insurance ratio
|
Loss ratio
|
Insurance payment/Premium receipt
|
|
Expense ratio
|
Expense/Premium receipt
|
|
Combined ratio
|
(Insurance payment+Expense)/Premium receipt
|
|
Combined ratio after dividends
|
(Insurance payment+Expense+Dividend)/Premium receipt
|
|
Operating ratio
|
(Insurance payment+Expense+Dividend-Investment income)/Premium receipt
|
**생명보험업은 손해보험업에 비해 더 낮은 자본을 요구
▶Rating updates
|
Positive
|
등급 상향 가능성 多
|
|
Negative
|
등급 하향 가능성 多
|
|
Stable
|
등급 변화 없을 가능성 多
|
|
Developing
|
등급이 변할 것 같지만 방향성은 모름
|
▶IPO Methods
|
Firm commitment
|
주관사가 남은 것들 모두 인수 → Trading profit
|
|
Best efforts
|
일정 부분까지 판매 시 인수 의무 없음
|
|
Dutch option
|
높은 가격에서 시작해 점차 낮아짐
수량이 모두 떨어지면 가장 낮은 가격으로 모든 물량 판매
|
▶LTCM
High Correlation risk/High Economic leverage (Not balance sheet leverage)
▶Basel Ⅱ/Ⅲ
|
Basel Ⅱ
|
Trading/Lending 활동도 자본 적정성 평가에 포함
|
|
Basel Ⅲ
|
Systematic/Non-systematic risk 모두 고려
|
▶BA/SA Operational risk capital requirement
Business indicator
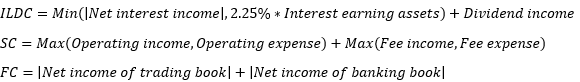
|
BIC Weight
|
Business
|
|
12%
|
Retail, Asset management
|
|
15%
|
Commercial, Agency
|
|
18%
|
IB (Corporate finance), Payment&Settlement, Trading
|
▶Data architecture
|
Semantic
|
의미론적
|
|
Conceptual
|
가장 추상적
|
|
Logical
|
Not concerned with implementation
|
|
Physical
|
구체적, Conceptual/Logical data를 Implementable data로 변환
|
▶Validation/Test set
|
Validation set
|
Two alternative models 중 더 월등한 모델 결정
|
|
Test set
|
선택된 모델의 Effectiveness 확인
|
▶Operational loss data from data vendors
Biased forward large losses and useful in determining loss severity
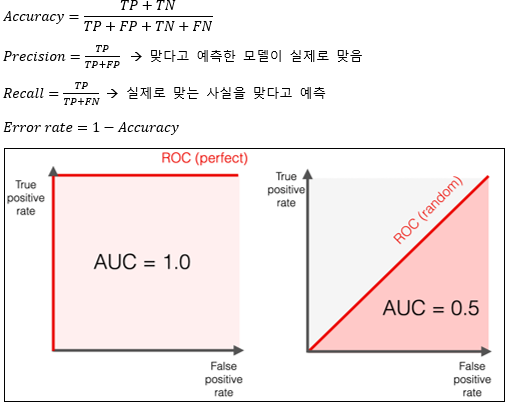
▶Confusion matrix/AUC
|
Confusion matrix
|
Model prediction
|
||
|
Positive (P)
|
Negative (N)
|
||
|
Actual
|
Positive (P)
|
TP
|
FN (TypeⅡ)
|
|
Negative (N)
|
FP (TypeⅠ)
|
TN
|
|
▶Unexpected loss risk management
Expected loss에 비해 주관성이 많이 개입되어 Risk manger의 판단이 Decision-making에 영향을 줌
▶Political risks
Democracy (민주주의): Continuous policy change, Frequent-Small changes
Autocracy/Authoritarian (독재): Discontinuous policy change, Rare-Large changes
▶RAROC
내부적 사업성 평가에 사용 (Not external comparison)
▶Risk management failures case study
|
Liquidity crisis
|
|
|
Lehman
|
단기 차입으로 비유동적 장기 자산 투자 (CDO)
|
|
Continental Illinois
|
Oil&Gas Market player, 높은 금리로 단기 자금 조달 실패
|
|
Nothern Rock
|
OTD Business Bank
|
|
Hedging crisis
|
|
|
Metallgesellschaft
|
장기공급계약 (Short)을 단기 선물 (Long)으로 롤링 헤지
마진 콜 발생 후 유동성 부족
|
|
Model risk crisis
|
|
|
Niederhoffer
|
Deep OTM Put 판매 → 극단적 상황 발생 (1일 7% 하락)
모델에서는 거의 불가능한 확률이 발생함
|
|
LTCM
|
비유동 국채 매수, 유동 국채 매도 전략 → 스프레드가 오히려 커지며 손실
|
|
London whale
|
VaR Limit을 조작
|
|
Rogue trading crisis
|
|
|
Barings Bank
|
Leeson이 회사 지시를 무시한 채 방향성 투기, 회계 조작
|
|
Reputation risk crisis
|
|
|
Volkswagen
|
테스트에서만 이산화탄소 저감 장치 장착
|
|
Governance crisis
|
|
|
Enron
|
부정 회계, 감사 실패, Not independent governance
|
|
잘못된 금융공학 상품 사용
|
|
|
Bankers Trust
|
이자율 파생 상품
|
|
Orange County
|
FRN 상품
|
|
Sachsen Landes Bank
|
Subprime 증권화 상품 투자
|
**글로벌 금융위기 이후 Fannie Mae/Freddie Mac → Nationalized, Discount window를 IB에도 개방
▶Zero-sum game
전체적으로 볼 때 위험 관리는 Risk elimination이 아닌 위험을 다른 상대로 분산시키는 Zero-sum game
▶Credit risks
|
Default risk (Insolvency)
|
Nonpayment of interest and principal → Cash-flow difficulties
|
|
Bankruptcy risk (Fail)
|
Collateral is not sufficient → Stop operating
|
|
Settlement risk
|
파생 상품 Payment risk
|
▶Risk/Reward trade-off
유동적/복잡하지 않은 상품일수록 Trade-off 관계가 분명
▶Risk Transfer/Mitigation
Transfer: 파생상품, 보험 등을 활용해 손실을 분산 (Zero-sum)
→ In practice, hedging with derivatives may not be a zero-sum game
Mitigation: 내부통제, 자산배분, 담보 확보를 통해 위험 관리
▶Risk appetite
Qualitative>Quantitative
질적 분석만으로 설정하는 경우도 존재
▶Lessons from global financial crisis
1. Need to prioritize stakeholder interests
2. Board/Risk committee should management compensation regimes
▶APT multifactor models
Flexibility, 다양한 변수들 사용 가능, 잘 분산된 포트폴리오에서 사용하기 좋음
▶Silo-based vs ERM
|
Silo-based
|
Overhedging/Excessive insurance problems, Isolated, Not integrated
|
|
|
ERM
|
Target
|
Risk appetite
|
|
Structure
|
Governance (CRO, Board, Audit)
|
|
|
Identification
|
VaR, Stresstesting
|
|
|
Risks are managed within each risk units but centralized at the senior management level
|
||
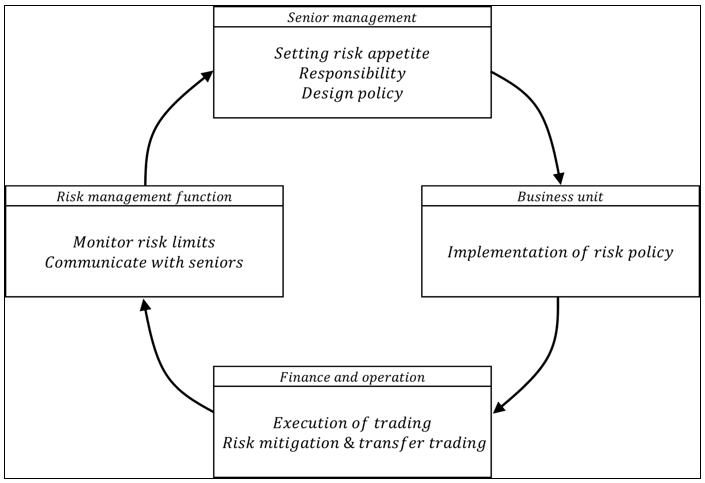
▶Interdependence of functional units
▶Credit/Interest rate risk mitigation
|
Credit risk
|
Marking-to-market
|
일일정산
|
|
Exposure netting
|
파생 상품 거래 금액의 상계로 Exposure 감소
|
|
|
Loan syndication
|
여러 기관이 함께 대출을 해주어 Exposure 감소
|
|
|
Termination clause
|
사건 발생 시 계약을 종료하여 위험 상황에서의 리스크 감소
|
|
|
Interest rate risk
|
Call feature
|
Call option을 통해 이자율 변동 위험 관리
→ 이자율 하락 시 기존 채권 상환 후 더 낮은 이자율로 다시 발행
|
▶Risk advisory director
다른 산업 관련 전문가
Chapter 2
Quantitative analysis
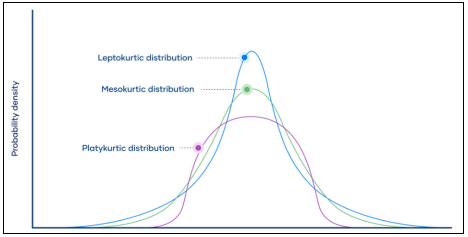
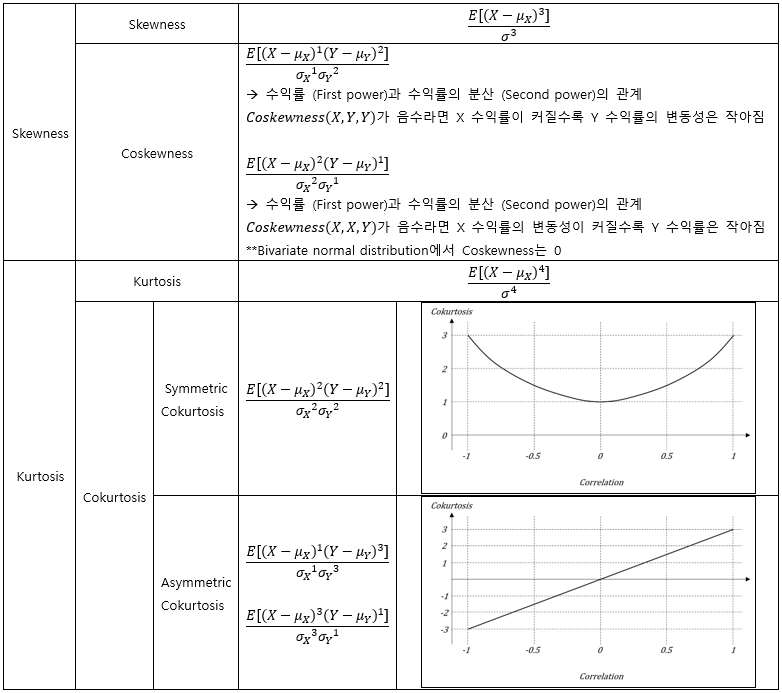
▶Skewness/Kurtosis
Positive Skewness → Mode<Median<Mean
Leptokurtic: Excess kurtosis>0 → Fatter tail
Platykurtic: Excess kurtosis<0
▶Heteroskedastic/Multicollinearity
|
Heteroskedastic
|
Multicollinearity
|
|
여전히 Unbiased/Consistency 특성 만족
하지만, OLS의 동분산 가정을 위반
|
OLS의 가정을 위반하지는 않음
|
|
Efficiency 특성 위배 → BLUE가 아니게 됨
|
Standard error가 커지는 문제점 발생
|
|
Unconditional heteroskedastic → Not major problem
Conditional heteroskedastic → Problem
|
▶White-test: Heteroskedastic 검정
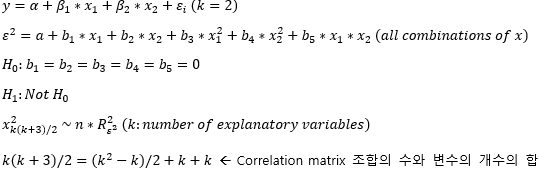
▶White noise
|
Types
|
Normal distribution
|
Independency
|
|
Gaussian (Normal) white noise
|
O
|
O
|
|
Independence (Strong) white noise
|
X
|
O
|
▶Seasonality
1. Dummy variable
전체 기간보다 하나 적은 Dummy variables 추가 Ex) 분기 계절성 반영 시 3개의 Dummy 추가

2. AR/MA Model: 계절성을 반영하는 Lag variable 추가
3. ARMA Model: ACF가 점진적으로 감소하는 경우 사용 가능
▶Bootstrapping
|
특징
|
Replacement
Direct use of data (Monte-carlo simulation → Indirect use of data)
|
|
Mehods
|
1. Bagging
2. Random Forest: No replacement, Many Decision-trees
3. Boosting (Gradient/Adaptive): 이전 결과에서 틀린 것은 더 높은 가중치, 맞은 것은 더 낮은 가중치 부여
|
|
(-)
|
Hard to consider dependency (CBB로 완화)
More outliers (Fatter distribution)
|
▶Omitted variable bias
|
중요하지 않은 변수의 추가
|
Standard error 증가
여전히 Unbiased estimator 만족
|
|
중요한 변수의 누락
|
누락된 변수의 효과가 오차항에 Capture → 오차항의 독립성 위배
OLS의 본질적 문제 발생으로 회귀분석 불가능 → Biased
Correlation이 클수록 더 큰 Bias, Correlation의 +/-에 따라 Bias의 방향에 영향
|
** Omiited variable bias는 Sample size와 관계없이 발생
▶Unbiased/Biased estimator
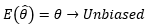
표본평균: Unbiased estimator
표본분산: Biased estimator 하지만, n-1로 나누어주면 Unbiased 만족
▶Ridge/LASSO//LARS
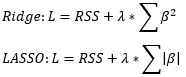
λ가 증가하면 β를 감소시키거나 (Ridge), 0으로 대체하여 (LASSO) Overfitting 방지
LARS: 모든 β를 0으로 두었다가 설명력이 높은 경우 키워나감
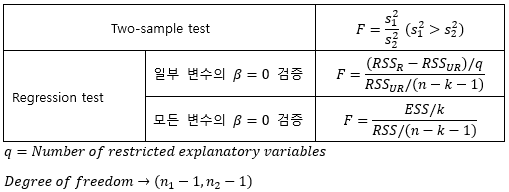
▶F-statistic
▶AR model: mean-reverting level
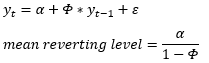
▶JB-test
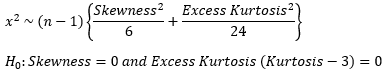
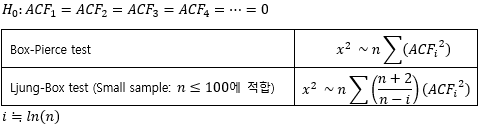
▶ACF

▶ACF test
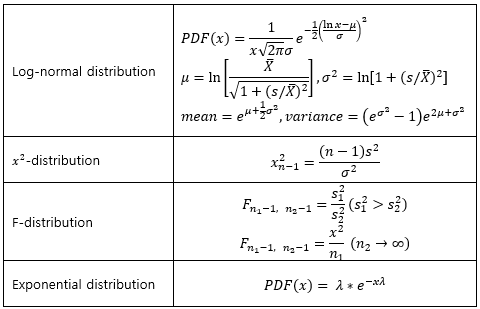
▶Log-normal distribution/x2-distribution/F-distribution/Exponential distribution
▶Penalize number of parameters
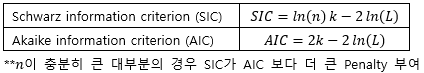
▶Monte-carlo 효율성을 높이기 위한 방법
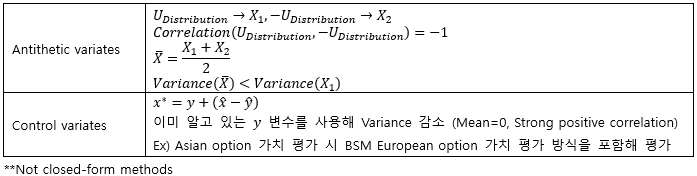
▶Correlation types
|
Spearman correlation
|
순위의 Correlation
|
|
Kendall’s Tau
|
크기의 대소 관계가 일치하는 정도에 따라 Correlation 파악
|
**Normal distribution에서는 Rank correlation과 Pearson’s correlation이 같음
▶ADF 검정

▶Conditionally independent
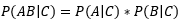
서로 독립적인 사건이라도 조건부 독립은 성립될 수도 안 될 수도 있음
▶Total probability rule
Mutually exclusive: 상호 배타적 사건
Exhaustive: 사건들의 확률 합이 100%
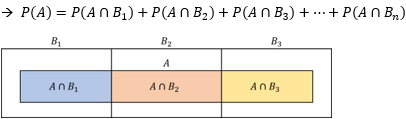
▶Interquartile range
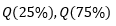
▶Multiple testing
유의 수준 (TypeⅠError) 증가
▶Linear transformations

▶Law of large number/Central limit theorem
|
Requirements
|
Mean finite
|
Variance finite
|
|
Law of large number
|
O
|
X
|
|
Central limit theorem
|
O
|
O
|
▶Cokurtosis/Coskewness
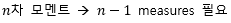
|
1차 모멘트
|
Mean
|
|
2차 모멘트
|
Covariance
|
|
3차 모멘트
|
Coskewness
|
|
4차 모멘트
|
Cokurtosis
|
▶Linear regression
Coefficients (α, β) must be linear
Not necessarily for the variables (x, y) → 비선형 데이터를 Log 등을 활용해 선형 분석 가능
▶Adjusted R2
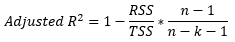
▶VIF

▶Bias-Variance trade-off
|
General-to-specific model
|
많은 변수의 모델로 시작한 뒤 가장 작은 t 통계량의 변수부터 제거해감
|
|
m-fold cross-validation
|
m-1개의 Training set, 1개의 Validation set
|
▶Residual plots
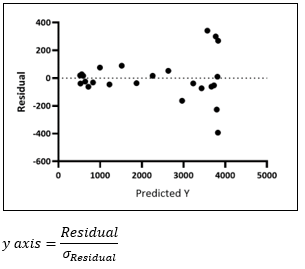
±4 Standard deviations를 넘는 경우 Problematic
▶Reinforcement learning
학습이 증가할수록 Exploitation (아는 행동) 증가하고 Exploration (새로운 탐색) 감소
|
States
|
Environments
|
|
Actions
|
Decisions
|
|
Rewards
|
Maximize reward
|
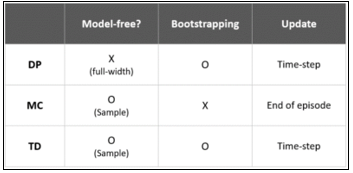
1. Monte carlo method (MC)

2. Temporal difference method (TD)
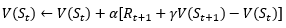
실시간으로 값을 갱신할 수 있음
▶Lag operators
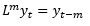
AR process is covariance stationary only if its lag polynomial is invertible
▶Power law
Slow declines in tail (Fat tail modeling)
▶Identifying outliers
No outliers → 회귀분석의 Assumption 중 하나
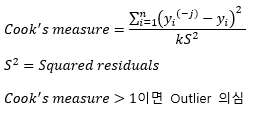
▶NLP
|
Tokenizing
|
Identifying only the words (Only lowercase)
|
|
Remove stopwords
|
the/has/a 같은 조사들 삭제
|
|
Stemming
|
어간으로 교체 (Arguing/Argued/Argues → Argu)
|
|
Lemmatizaiton
|
단어의 기본형으로 교체 (Worse → Bad)
|
|
N-grams
|
같이 있어야 의미가 명확한 것들은 같이 둠
|
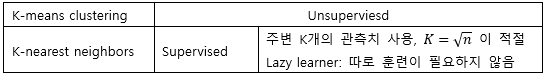
▶K-means/K-nearest neighbors
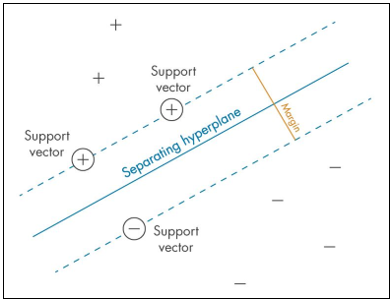
▶SVM
▶Neural networks
Find non-linear relationship
Gradient descent algorithm:
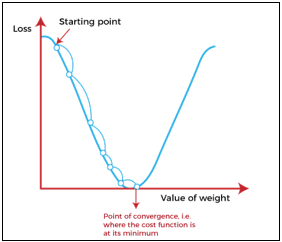
Input의 Weights를 조정해가며 Loss function이 가장 작아지는 경우를 찾음
‘기울기>0’ 인 경우 Weight를 줄이고, ‘기울기<0’ 인 경우 Weight를 늘림
Learning rate (이동간격)이 너무 클 경우 값이 수렴하지 않을 수 있으며 너무 작을 경우 Cost 多
Training set의 Loss function이 증가하더라도 Validation set에서 감소하면 → Stop gradient descent algorithm
(Overfitting 방지)
Chapter 3
Financial markets and products
▶Interest rate swap valuation
|
액면 금액
|
$2,000,000
|
|
Fixed rate
|
7%
|
|
Payment
|
Semi-annual
|
|
Tenure
|
Spot
|
FRA
|
|
6-month LIBOR
|
6.5%
|
6.5%
|
|
12-month LIBOR
|
6.8%
|
7.1%
|
|
18-month LIBOR
|
7.5%
|
8.9%
|
Method 1
|
Tenure
|
6-month
|
12-month
|
18-month
|
|
Fixed cash flow
|
70,000
|
70,000
|
70,000+2,000,000
|
|
Floating cash flow
|
(65,000+2,000,000)
|
|
|
|
Net cash flow
|
(1,995,000)
|
70,000
|
2,070,000
|
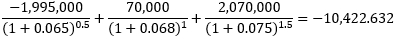
현재 Floating-rate reset date라면 Floating-rate payments의 가치는 액면 금액과 동일
|
Tenure
|
6-month
|
12-month
|
18-month
|
|
Fixed cash flow
|
70,000
|
70,000
|
70,000+2,000,000
|
|
Floating cash flow
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash flow
|
70,000
|
70,000
|
2,070,000
|
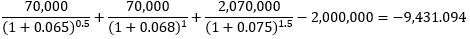
Method 2 (FRA 적용)
|
Tenure
|
6-month
|
12-month
|
18-month
|
|
Fixed cash flow
|
70,000
|
70,000
|
70,000+2,000,000
|
|
Floating cash flow
|
(65,000)
|
(71,000)
|
(89,000+2,000,000)
|
|
Net cash flow
|
5,000
|
(1,000)
|
(19,000)
|
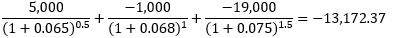
▶Box spread
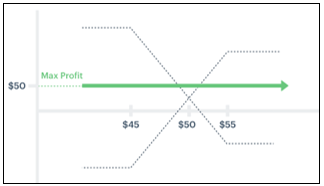
Bull call spread+Bear put spread (초기에 옵션 프리미엄을 지불하고 포지션 형성)
Max profit=두 행사가의 차이
Max profit=초기 옵션 프리미엄 지불액: 무차익거래
Max profit>초기 옵션 프리미엄 지불액: Box를 Long하여 차익거래 가능
▶Strip/Strap
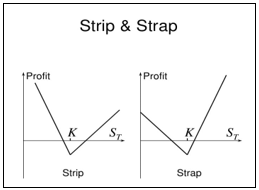
Strip은 Straddle에서 Put option을 하나 더 매수하여 하락에 베팅
Strap은 Straddle에서 Call option을 하나 더 매수하여 상승에 베팅
▶Delta
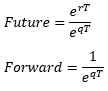
▶Bond returens
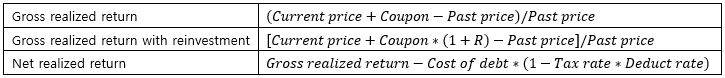
▶Eurodollar future

|
Eurodollar future
|
일일정산
기초에 이자 지급
|
|
FRA
|
마지막에만 거래
기말에 이자 지급
|
▶Bond classification
|
Clauses
|
||
|
Mortgage
|
After-acquired clause: 이미 담보된 자산을 다시 담보로 대출 불가
|
|
|
Debentures
|
무담보 대출
Negative-pledge clause: 이후 담보 채권 발행 시 해당 채권도 담보가 설정되어야 함
|
|
|
Retiring methods
|
||
|
Call
|
Fixed call: 정해진 행사가가 초기엔 높았다가 액면가로 수렴
Make-whole call: 잔존 현금흐름의 현재가치보다 높은 가격으로 행사가격 설정
|
|
|
Sinking fund
|
매년 원금 분할 회수, 담보 가치가 하락하는 경우 담보 비율 유지 가능
|
|
|
Maintenance&Replacement
|
담보 비율이 유지되도록 하는 조항
|
|
|
Tender offer (공개매수)
|
채권을 다시 사들임 (많이 사용되는 방식)
|
|
|
Start-Up company
|
||
|
Deffered-coupons
|
할인 판매, 이자를 나중에 지급
|
처음에 지급 부담이 적고
나중에 부담이 많아짐
|
|
Step-up
|
Coupon 점차 증가
|
|
|
Payment-in-kind
|
Coupon 대신 채권을 추가 지급
|
|
|
Extendable reset bonds
|
발행 이후 신용도 상승 시 금리를 낮추어 줌
|
처음에 지급 부담이 높지만 나중에 신용도 상승으로 부담이 낮아짐
|
▶Exotic options
Gap option
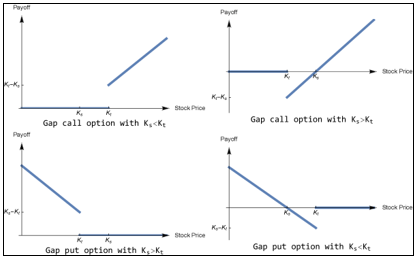
Compound option: More Leveraged/Sensitive
▶Cheapest-to-deliver Bond
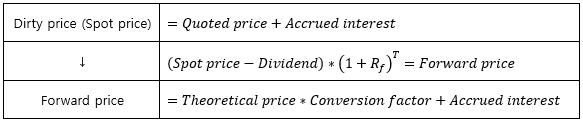
|
Upward yield curve/Interest rate>6%
|
Low-coupon, Long-maturity → CTD
|
|
Downward yield curve/Interest rate<6%
|
High-coupon, Short-maturity → CTD
|
**Wild card play: Short position 보유자가 Deliver 일자를 결정하여 Delivery cost 감소
→ Future price 감소로 Short position에게 유리
▶Swap payer/FRA long
Swap payer: Fixed payment payer, Floating payment receiver
FRA long: Floating payment receiver
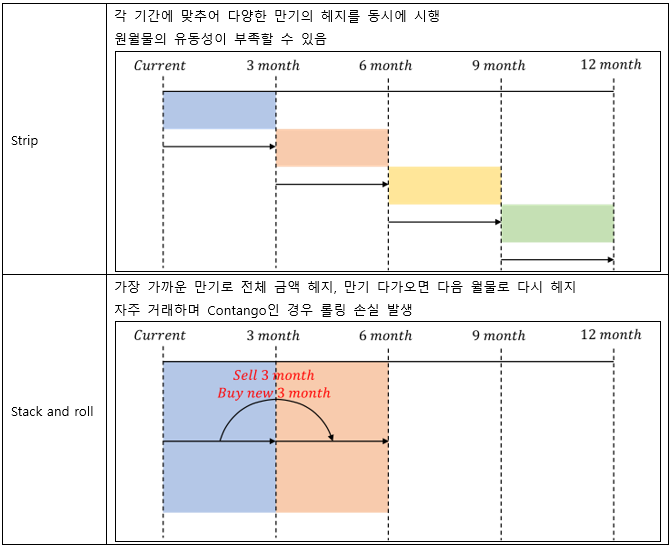
▶Strip/Stack and roll hedge
▶Increasing prepayment speed
|
Interest rate ↓
|
Prepayment speed ↑
|
|
House price ↑
|
Prepayment speed ↑
|
|
Mortgage size ↑
|
Prepayment speed ↑
|
|
만기 ↓
|
Prepayment speed ↑
|
|
Default ↑
|
Prepayment speed ↑
|
▶Zero-cost option (Zero premium)
초기에 프리미엄을 지급하지 않고 행사/만기일에 실현 손익과 프리미엄에 이자율을 적용한 금액을 함께 계산
▶Japanese bond yield
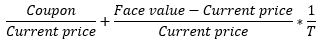
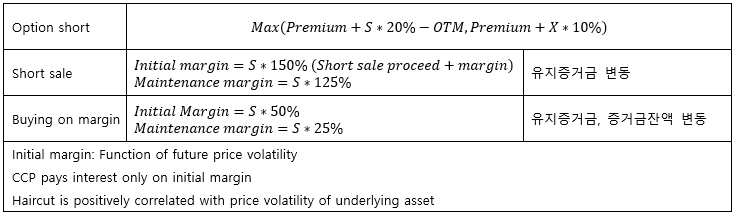
▶Margining
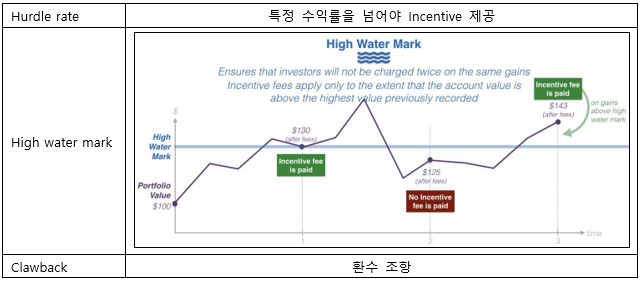
▶Hedge funds compensation clauses
▶PPP
자국 물가>외국 물가
→ 물가 차이만큼 자국 통화 가치 하락
▶Commodity future
|
Storage cost
|
농작물, 액화가스 등의 상품에서 높은 Storage cost를 보임
Metal → 보관 용이 Storage cost가 낮음
|
|
Lease rate
|
Commodity의 경우 Lease 상대의 파산으로 음수가 되는 경우도 존재
(Future price 증가)
→ 이 경우 Arbitrageurs는 Buy spot commodity, Sell future commodity를 통해 이익
|
|
Convenience yield
|
Added to lease rate
상품을 보유하며 얻는 Non-monetary benefit
|
▶Hedge accounting
1. Documented
2. 헤지 대상과 헤지 상품 간의 Reasonable한 관계
→ Hedge instrument의 이익/손실을 헤지 대상과 함께 이연하여 보고할 수 있음
▶Options
1. 주로 개별 주식 옵션은 American-style/인덱스 옵션은 European-style
2. 개별 주식/인덱스 옵션은 대부분 실물 인도가 아닌 현금 거래로만 이루어짐
▶Exotic option
1. Versatile and More efficient hedging
2. Better reflect a firm’s view on factors
3. Used for Tax/Regulatory purpose
▶FX exposure
|
Transaction
|
선물/선도환 등의 파생 상품을 통해 헤지 가능
|
|
Translation
|
해외 보유 자산의 가치 평가, Local에서의 Financing을 통해 자산을 구매하여 헤지
|
|
Economic
|
환율 변동에 의한 수요, 상품 가격 경쟁력 변화
외국에 생산 시설을 이전, 수출 통로 다변화 (가장 헤지하기 어려움)
|
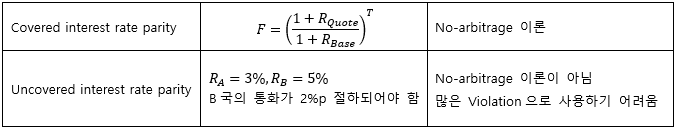
▶Interest reate parity
▶DB형/DC형 연금
|
DB
|
하나의 계좌로 모아서 운용
|
|
DC
|
각 고객의 계좌로 운용
|
▶Closed/Opened funds
|
Closed
|
Opened
|
ETF
|
|
주식 수 고정
다른 투자자들과 거래
|
주식 수 유동
새로운 투자자 진입 → 주식 수 증가
투자자 유출 → 주식 수 감소
펀드 회사와 직접 거래 (장내 거래)
|
주식처럼 개장 시간에 거래 가능
다양한 거래 방식 사용 가능
(Short selling, Stop order, Limit order)
|
|
NAV가 아닌 다른 가격으로도 거래가 가능
|
매일 PM 4:00에 NAV 계산
거래 전까지 가격을 알 수 없음
(Poor price visibility)
|
|
|
Management fee (연 보수)
Sales charge (판매수수료):
Front-end, Back-end
|
||
|
Long/Short 전략 모두 사용
|
Long 전략만 가능
|
|
|
분기에 1번 보유 종목 공개
|
매일 두 번 보유 종목 공개
|
▶Day count convention
|
U.S. treasury bond
|
Actual/Actual
|
|
Money-market instruments (Treasury bills)
|
Actual/360
|
|
Corporate bond
|
30/360
|
▶Undesirable trading behaviors
|
종류
|
설명
|
불법 여부
|
|
Late trading
|
PM 4:00이후 거래
|
Illegal
|
|
Front running
|
선행 매매
|
Illegal
|
|
Market timing
|
시장가와 NAV의 괴리를 이용한 이익 추구 거래
펀드 자산의 급격한 변동이 생길 수 있어 충분한 유동성 필요
|
Not illegal
|
|
Directed brokerage
|
펀드 판매사와 펀드 회사 간의 Rebate → 시장의 신뢰 하락
|
Not illegal
|
▶Central clearing
거래 상대방 파산 시 담보물을 시가에 매각하여 Close-out하기 보단 Auction을 진행
Initial margin → 거래 상대방의 신용도가 아닌 거래의 특성, 상품 종류 등에 따라 결정됨
|
Risks
|
|
|
Default correlation is high for OTC derivatives
|
극단적 상황에서 큰 손실의 위험
|
|
OTC derivatives are priced by model
|
Model risk of pricing derivatives
|
|
Legal risk of netting (서로 다른 지역의 회사들 사이의 Netting)
|
|
|
System failure
|
|
▶Tailing the hedge
현/선물 가격 변화에 맞추어 헤지 계약 수 조정
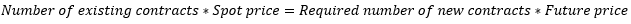
▶Foreign currency future quote
Spot quote Bid/Ask: 1.2944/1.2952
Forward points quote Bid/Ask: 56.34/58.85 (0.0001 곱하기)
→ Forward quote Bid/Ask: 1.2944+0.005634/1.2952+0.005885 → 1.30034/1.301085
**82.4012 JPY price of CAD → 82.4012 JPY/CAD
▶LEAPS option
매년 1월이 만기인 장기 옵션
▶Principal protected notes (PPNs)
할인채와 콜 옵션을 동시에 매수해 Protective put과 비슷한 수익 구조 만듦
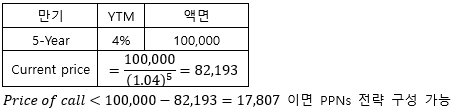
▶Expected return
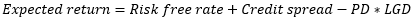
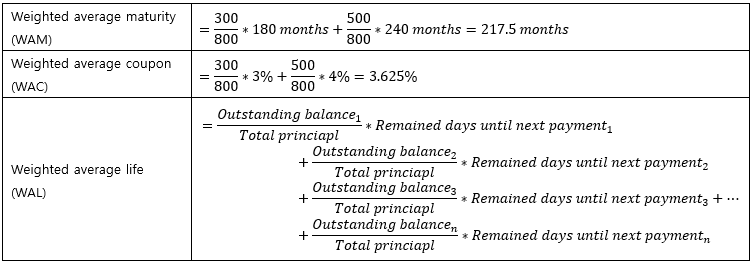
▶Pass-through securities
▶TBA
|
Specified pools
|
Pool의 자산이 거래 전에 명확히 파악됨
|
|
TBA
|
Pool의 자산이 거래 2일 전까지 공개되지 않고 거래부터 수행
|
▶PAC and Support tranche
Support tranche가 Prepayment risk를 감수 → 그 이상의 손실은 PAC으로 넘어감 (Broken/Busted PAC)
▶Dollar roll transaction
Month 1에 Pool 판매, Month 2에 Pool 구매

▶Incentive function of prepayments
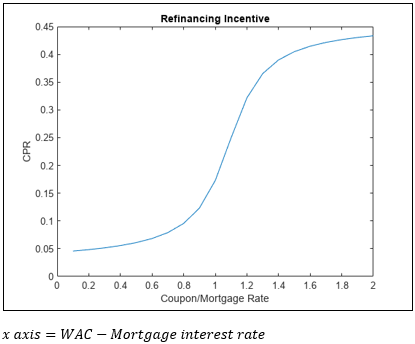
현재 지불하는 Coupon rate (WAC)가 새로운 모기지 대출 금리보다 너무 높다고 생각되면 Refinancing 수요 증가
▶Backfill bias
Hedge fund가 성과를 보고할 때 이전의 성과들도 함께 포함됨
Chapter 4
Valuation and risk models
▶MDE(Multivariate density estimation)
|
특징
|
Non-parametric
현재와 유사한 과거 데이터에 더 큰 가중치 부여
|
|
(+)
|
현재 시장 환경 반영
Dependency 반영
|
|
(-)
|
Overfitting
많은 데이터 필요
|
▶Gini measure: Information gain of decision tree method
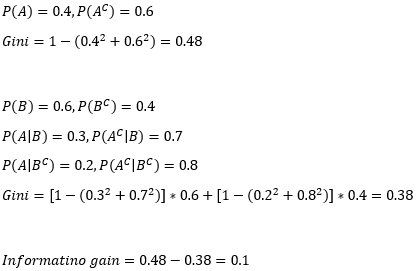
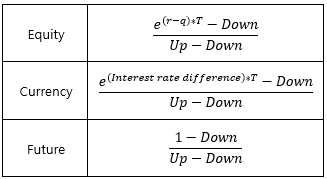
▶Binomial-Tree upward movement probability
▶Distribution of recovery rate
Bimodal (쌍봉) distribution
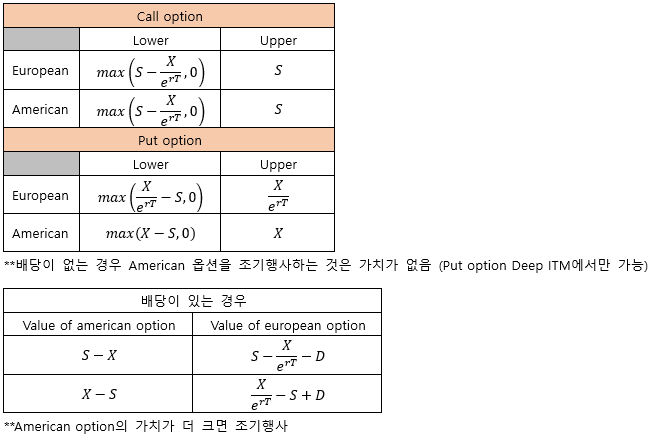
▶American/European options value
▶Forward/Spot/Par rate

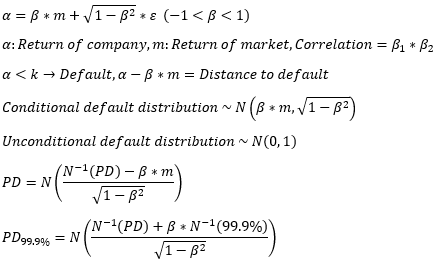
▶Vasicek model (Single-factor model)
▶Key rate 01/Forward bucket 01

▶Coherent risk measure

▶Relation of PD and LGD
PD와 LGD는 Positive correlation
▶Impact of credit rating change
등급 상향보다 등급 하향에 더 민감하게 반응
Watchlist downgrade impact (중/단기)>Outlook downgrade impact (장기) and Actual downgrade impact
▶Stressed VaR
1. Conditional risk measure: Stress 상황에서의 데이터만 사용 → 각 은행마다 다른 기간 사용
2. Short estimation period (1~10 Days)
3. Use Historical simulation approach
▶Portfolio σ (모든 Pair가 같은 상관계수를 가진 경우)
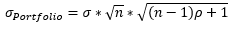
▶Credit rating
1. Ratings for companies whose debt instruments are publicly traded
2. Periodically Reaccess
3. Rating 받는 회사가 Fee 지불 (Not investor → Conflicts of interest)
▶Component of bond’s Profit&Loss
|
Tenure
|
0.5
|
1.0
|
1.5
|
2.0
|
|
Coupon
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
101
|
|
Bond spread
|
|
|
Beginnig
|
Ending
|
|
0.3%
|
0.2%
|
|
Forward rate
|
Beginnig
|
Ending
|
|
0~0.5
|
0.8%
|
0.7%
|
|
0.5~1.0
|
1.4%
|
1.0%
|
|
1.0~1.5
|
1.8%
|
1.2%
|
|
1.5~2.0
|
2.1%
|
2.0%
|
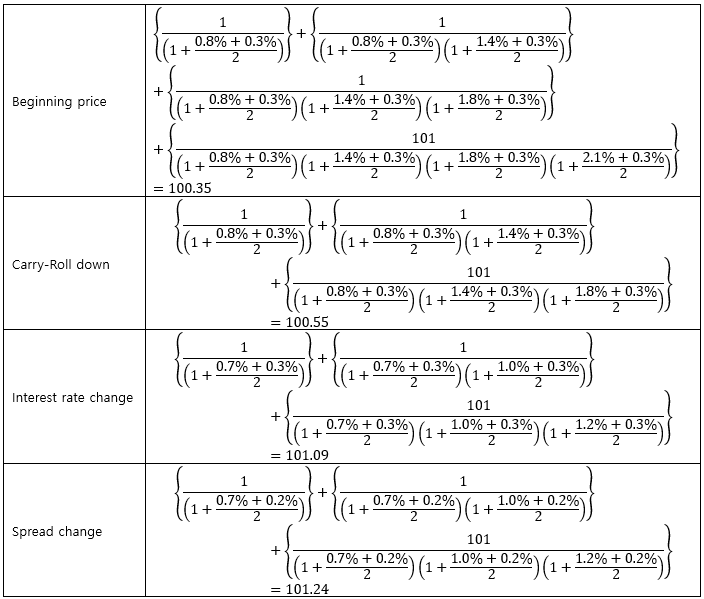
▶오일러 정리의 활용
|
Loans
|
X1
|
X2
|
X3
|
|
VaR
|
10,000
|
8,000
|
9,500
|
|
Loan VaR 1% 증가에 따른
Portfolio VaR 증가량
|
58.1
|
65.6
|
α
|
|
Correlation
|
X1
|
X2
|
X3
|
|
X1
|
1.0
|
0.1
|
0.1
|
|
X2
|
0.1
|
1.0
|
0.8
|
|
X3
|
0.1
|
0.8
|
1.0
|
**Portfolio VaR=20,300
What is the contribution of Loan X3 to the Portfolio VaR?
Method 1 (공헌 VaR 사용)
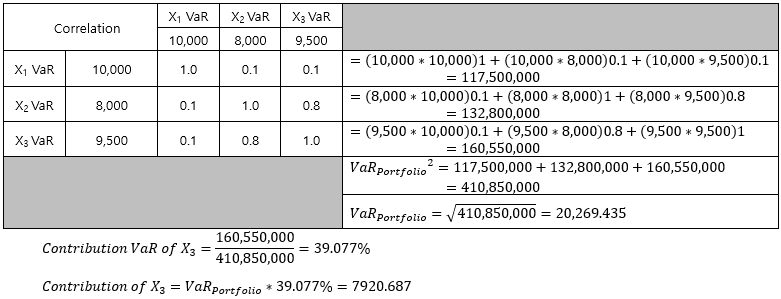
Method 2 (오일러 정리 활용)
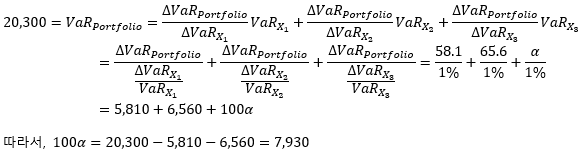
▶Covariance
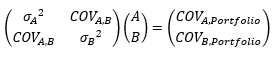
▶ES
ES surface curve showing the interactions of both adjustments (Holding period/Confidence level) is convex
▶Fat-tail
Aggregation of Normal/Non-normal conditional distributions → Fat-tail Unconditional distribution
▶Actual loss/EL/UL
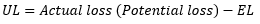
▶Stresstesting validation
Testing data during both stressed and non-stressed periods
▶Par rate
채권의 현재가격이 액면가와 동일해지도록 하는 Coupon rate
▶Coupon rate vs YTM
Coupon rate<YTM: 할인되어 거래
Coupon rate>YTM: 할증되어 거래
▶Barbell/Bullet strategy
|
Barbell strategy
|
High convexity, Volatile interest/Parallel increase interest rate인 경우 선호됨
|
|
Bullet strategy
|
Non-parallel changes in interest rate인 경우 Bullet 전략이 보통 Outperform
|
▶Carry-roll-down scenarios
1. Realized forward scenario
|
Period
|
Forward rate
|
Realized forward rate after 6 months
|
|
0-0.5
|
0.8%
|
|
|
0.5-1.0
|
1.0%
|
1.0%
|
|
1.0-1.5
|
1.2%
|
1.2%
|
|
1.5-2.0
|
1.4%
|
1.4%
|
2. Unchanged term structure scenario
|
Period
|
Forward rate
|
Realized forward rate after 6 months
|
|
0-0.5
|
0.8%
|
|
|
0.5-1.0
|
1.0%
|
0.8%
|
|
1.0-1.5
|
1.2%
|
1.0%
|
|
1.5-2.0
|
1.4%
|
1.2%
|
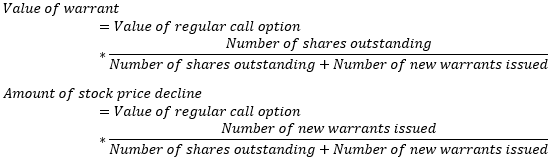
▶Warrants
▶Rho/Vega
Rho는 OTM보다 ITM에서 더 큼
잔존 만기가 클수록 Vega가 더 큼 (변동성에 영향을 받을 기간이 많음)
Vega: 변동성 1%p 변화에 따른 옵션 가격의 BP 변화
European Put ITM에서 θ>0일 수 있음
▶Merton model
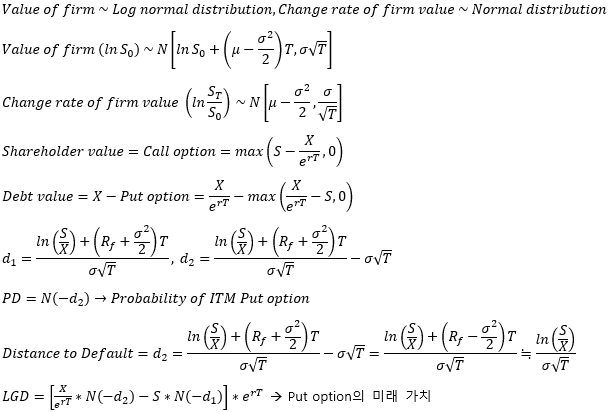
**Limitations
1. 비유동적/Non-public traded asset에 사용 불가
2. 변수들이 실시간으로 변하므로 끊임없이 계산되어야 함 (계산 비용 多)
3. 관측할 수 있는 변수여야 함
4. 갑작스러운 Default 반영 불가 (Jump-to-default)
5. Investment grade bond 보다 낮은 등급의 채권 평가에 적합